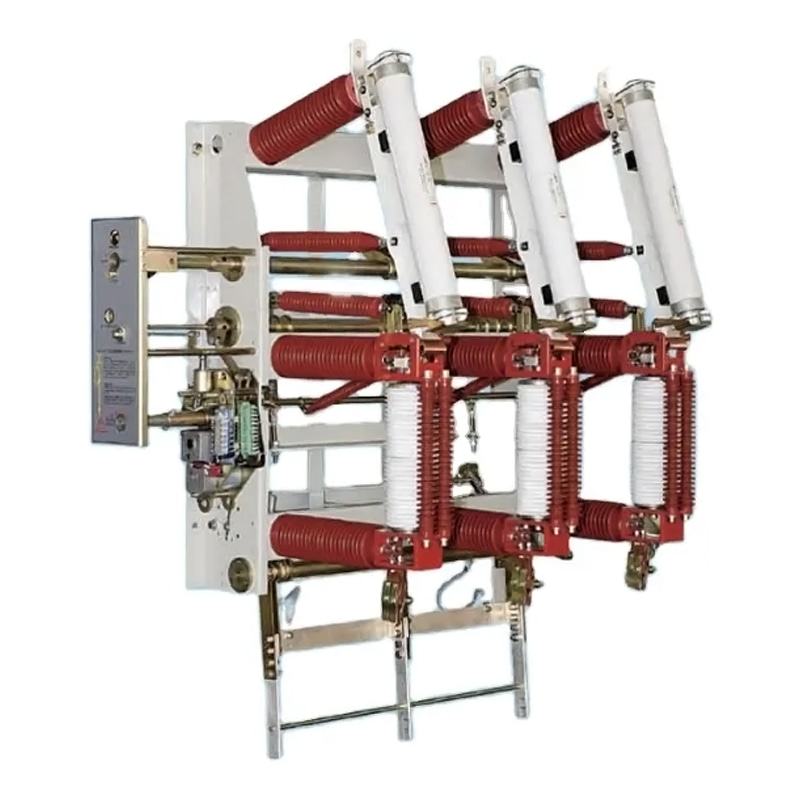
High voltage indoor lightning surge arresters are essential to safeguarding these systems, ensuring operational reliability and longevity.
Lightning surge arresters, also known as surge protectors or transient voltage surge suppressors, are devices designed to protect electrical equipment from over-voltage transients caused by external (lightning) or internal (switching) events. High voltage indoor lightning surge arresters specifically cater to high voltage systems within indoor environments, providing a vital line of defense against transient surges.
High Energy Absorption: These arresters are designed to handle substantial energy levels, efficiently dissipating the high-energy transients associated with lightning strikes.
Fast Response Time: The response time of a surge arrester is crucial. High voltage indoor models react almore instantaneously to surges, clamping down the over-voltage and protecting downstream equipment.
Thermal Stability: These arresters are built to withstand high temperatures generated during surge events, ensuring reliable performance even under bad conditions.
Compact Design: Indoor surge arresters are designed to fit within electrical panels and enclosures without requiring excessive space, facilitating easy integration into existing systems.
Maintenance-Free Operation: Modern high voltage indoor surge arresters are engineered for long-term reliability with small maintenance, making them a cost-effective solution over their operational lifespan.
Protection of Critical Equipment: By clamping down on transient over-voltages, these arresters protect sensitive electrical equipment, reducing the risk of damage and extending the lifespan of the equipment.
Enhanced System Reliability: Protecting the electrical system from lightning-induced surges helps maintain operational stability, small downtime and ensuring consistent performance.
Cost Savings: Preventing damage to electrical infrastructure reduces repair and replacement costs. Additionally, small downtime can lead to significant operational cost savings.
Safety Improvement: By managing over-voltage conditions effectively, surge arresters enhance the overall safety of the electrical system, protecting personnel and equipment from potential hazards.
Ease of Installation: High voltage indoor surge arresters are typically designed for straightforward installation, allowing for quick deployment and integration into existing systems.
High voltage indoor lightning surge arresters are utilized in various settings, including:
Utility Substations: These arresters are crucial in substations, protecting transformers and other critical components from lightning-induced surges.
Industrial Facilities: In industrial environments, surge arresters safeguard machinery and control systems, ensuring continuous and reliable operation.
Commercial Buildings: High voltage systems in commercial buildings, such as data centers and hospitals, rely on surge arresters to protect sensitive equipment and maintain uninterrupted service.
Renewable Energy Installations: Wind and solar power installations use surge arresters to protect inverters and other electrical components from transient over-voltages.
Telecommunication Infrastructure: To ensure reliable communication services, telecom facilities employ surge arresters to protect against lightning-induced surges that can disrupt operations.
When implementing high voltage indoor lightning surge arresters, several factors need to be considered:
System Voltage Rating: Ensure the arrester's voltage rating is compatible with the system it is protecting. Over-specifying or under-specifying the rating can lead to inadequate protection or unnecessary costs.
Discharge Current Rating: The arrester should be capable of handling the expected surge in current levels. This rating determines the arrester’s ability to dissipate the energy of a surge without sustaining damage.
Environmental Conditions: Consider the indoor environment where the arrester will be installed. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and potential exposure to dust or corrosive elements should be evaluated to ensure reliable operation.
Coordination with Other Protective Devices: The surge arrester should be coordinated with other protective devices in the system, such as circuit breakers and fuses, to ensure comprehensive protection.



 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى