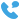
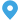
Sale Wholesale Transformer Substation Factory Manufacturer
Transformer substations are critical components of the electrical power infrastructure, responsible for the efficient distribution of electricity from power plants to consumers. These facilities are designed to step up or down voltage levels to ensure that power is transmitted and distributed safely and effectively. The role of transformer substations in the power grid is indispensable, as they facilitate the long-distance transmission of electricity with small losses.
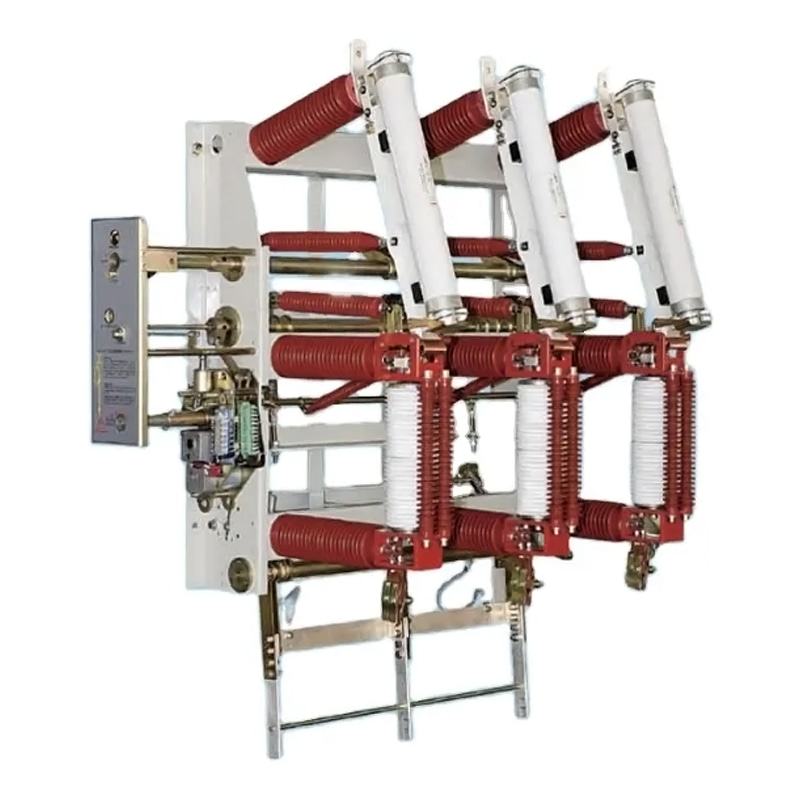
A typical transformer substation comprises several key components, including:
Transformers: The heart of the substation, transformers are responsible for adjusting voltage levels. They consist of coils of wire wrapped around a magnetic core, which can either increase or decrease the voltage of the electrical current passing through them.
Circuit Breakers: These devices are crucial for safety, as they automatically disconnect parts of the electrical system in the event of a fault, preventing damage and ensuring the continuity of power supply to other areas.
Switchgear: This equipment allows operators to control, protect, and isolate electrical equipment. It includes switches, fuses, and relays that help manage the flow of electricity within the substation.
Control Systems: Modern substations are equipped with advanced control systems that monitor and regulate the operation of the facility. These systems can automatically respond to changes in the power grid, ensuring good performance and reliability.
The primary function of a transformer substation is to transform voltage levels. Power plants generate electricity at high voltages to small energy loss during transmission. As the electricity approaches its destination, it must be stepped down to a level suitable for residential, commercial, or industrial use. Transformer substations perform this crucial voltage conversion.
There are several types of transformer substations, each serving a specific purpose:
Bulk Substations: These are large facilities that handle high-voltage transmission lines and are typically located near power plants.
Distribution Substations: Smaller in size, these substations step down voltage for distribution to local areas.
Regulating Substations: These substations are designed to maintain a stable voltage level in the power grid, adjusting as needed to compensate for fluctuations.
Safety is a paramount concern in transformer substations. The high voltages involved pose significant risks, and as such, substations are equipped with numerous safety features:
Fencing and Barriers: Physical barriers prevent unauthorized access to the substation, reducing the risk of accidents.
Insulation: Transformers and other equipment are insulated to prevent electrical shocks and short circuits.
Grounding: Proper grounding of equipment helps to dissipate electrical energy safely in the event of a fault.
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the reliability and longevity of transformer substations. This includes:
Visual Inspections: Regular checks for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage.
Preventive Maintenance: Scheduled servicing to replace worn parts and ensure the proper functioning of equipment.
Modernization: Upgrading older substations with new technology to improve efficiency and reliability.
Transformer substations must also consider their environmental impact. This includes:
Emission Control: Managing the release of gases and other emissions to small environmental harm.
Land Use: Efficient use of land to small the footprint of substations and reduce the impact on local ecosystems.
As technology advances, transformer substations are evolving to meet the demands of a modern power grid. This includes:
Smart Grid Integration: Incorporating smart grid technology to improve monitoring, control, and efficiency.
Renewable Energy Integration: Adapting to accommodate the variable nature of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power.
Sustainable Design: Incorporating sustainable practices in the design and operation of substations to reduce their environmental impact.
Transformer substations are essential for the reliable and efficient distribution of electricity. They play a critical role in stepping up and down voltage levels, ensuring that power reaches consumers safely and effectively.



 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى