Transformer Compact Secondary Substation Supplier Manufacturer Maker
Transformer substations are integral to the power distribution network, serving as the critical junctions where voltage is stepped up or down to meet the requirements of various consumers. These substations are designed to efficiently manage and control the flow of electricity, ensuring that power is delivered safely and reliably to homes, businesses, and industries.
Transformer substations are essential for maintaining the balance between power generation and consumption. They perform several key functions, including:
1. Voltage Regulation: Adjusting voltage levels to match the needs of different consumers and to minimize energy loss during transmission.
2. Power Distribution: Routing electricity to various distribution networks and ensuring that it reaches end-users efficiently.
3. System Protection: Implementing protective measures to safeguard the electrical grid from faults, short circuits, and other potential hazards.
4. Load Management: Monitoring and controlling the flow of electricity to meet fluctuating demand and maintain system stability.
A typical transformer substation consists of several key components, each playing a specific role in the overall operation:
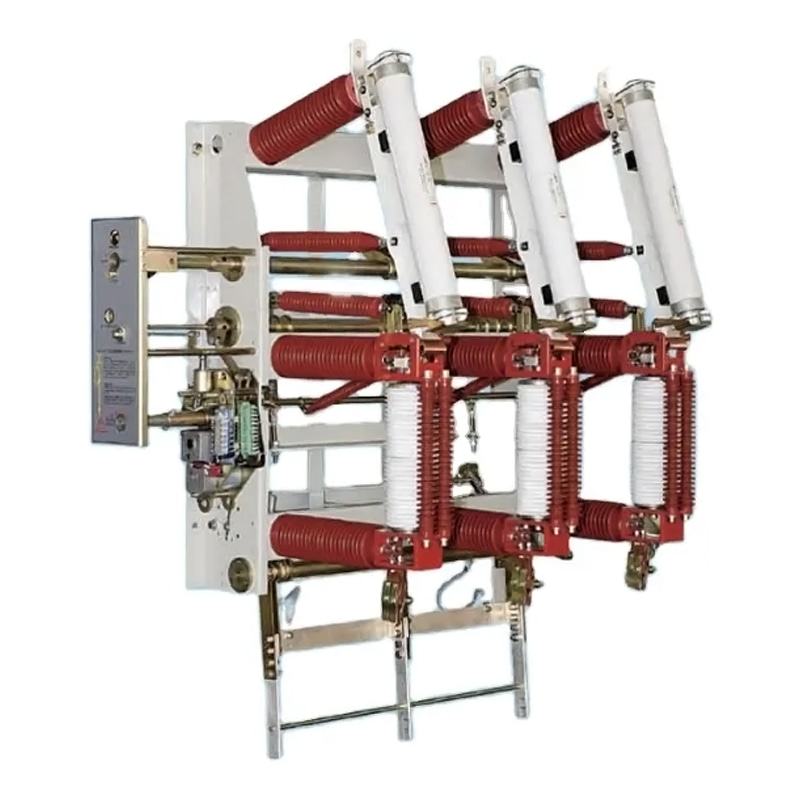
1. Transformers: The core component, transformers are responsible for stepping up or stepping down voltage levels as required.
2. Circuit Breakers: These devices automatically open the circuit in case of a fault, preventing damage to equipment and ensuring safety.
3. Switchgear: Used to control, protect, and isolate electrical equipment, switchgear is crucial for maintaining system integrity.
4. Control Systems: Modern substations are equipped with advanced control systems that monitor and manage operations remotely.
5. Protection and Relay Systems: These systems detect abnormal conditions and initiate protective actions to safeguard the grid.
6. Auxiliary Equipment: Includes cooling systems, lighting, and other support systems necessary for the substation's operation.
The design and layout of a transformer substation are critical to its performance and reliability. Key considerations include:
1. Site Selection: Choosing a location that minimizes transmission losses, provides easy access for maintenance, and meets safety and environmental regulations.
2. Space Optimization: Efficient use of space to accommodate all components while allowing for ease of operation and maintenance.
3. Redundancy: Incorporating redundant systems to ensure continued operation in the event of a component failure.
4. Scalability: Designing the substation to accommodate future expansion and upgrades as demand grows.
5. Environmental Impact: Minimizing the environmental footprint through the use of sustainable materials and energy-efficient designs.
The safe and efficient operation of a transformer substation requires regular maintenance and monitoring. This includes:
1. Routine Inspections: Regular visual inspections to identify any signs of wear, damage, or potential issues.
2. Preventive Maintenance: Scheduled maintenance activities to prevent equipment failure and extend the life of components.
3. Condition Monitoring: Utilizing advanced sensors and diagnostic tools to monitor the health of the substation in real time.
4. Upgrades and Modernization: Periodically updating equipment and systems to incorporate new technologies and improve performance.
5. Training and Safety: Ensuring that all personnel are adequately trained and follow safety protocols to minimize risks.
Transformer substations face several challenges, including aging infrastructure, increasing demand, and the integration of renewable energy sources. To address these challenges, the industry is focusing on:
1. Digital Transformation: Implementing digital technologies such as IoT, AI, and machine learning to enhance monitoring, diagnostics, and decision-making.
2. Smart Grid Integration: Developing substations that can seamlessly integrate with smart grid technologies for improved efficiency and reliability.
3. Energy Storage Solutions: Exploring energy storage options to manage peak demand and support the integration of renewable energy.
4. Environmental Sustainability: Adopting eco-friendly materials and practices to reduce the environmental impact of substations.
5. Cybersecurity: Strengthening the security of substation control systems to protect against cyber threats and ensure the integrity of the grid.



 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى