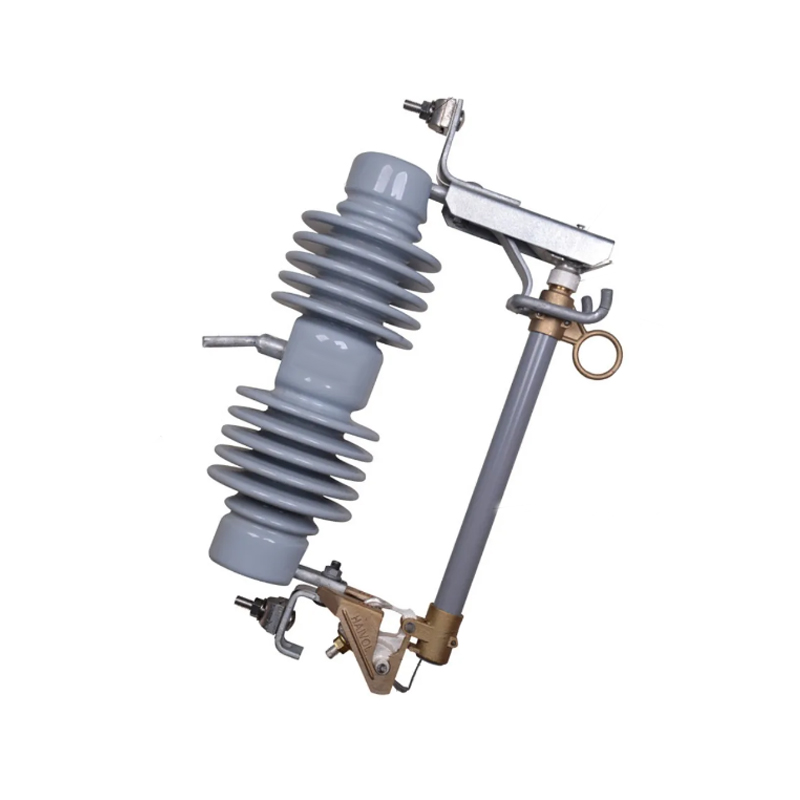
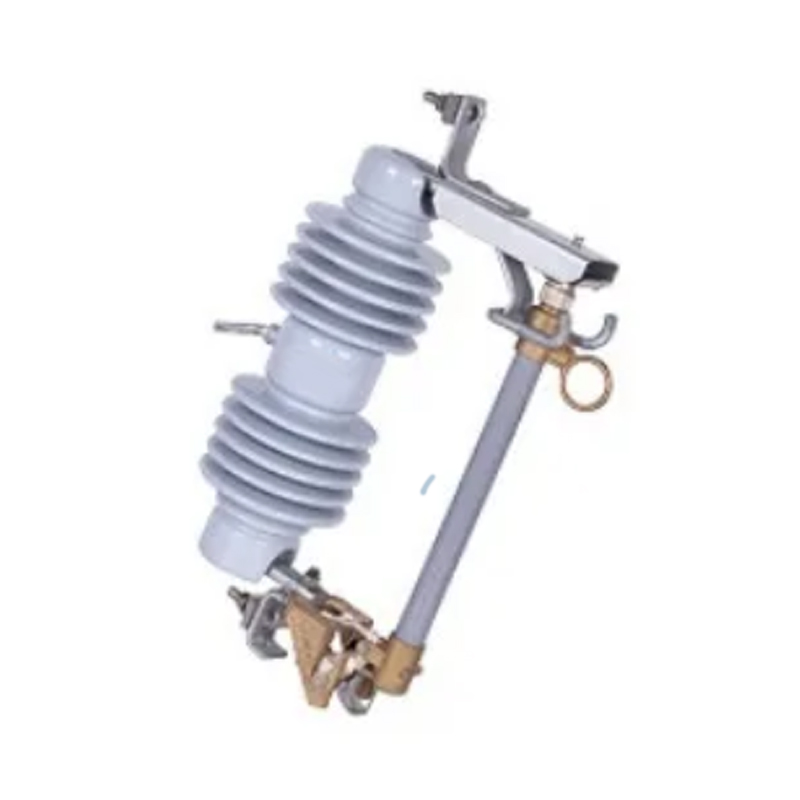
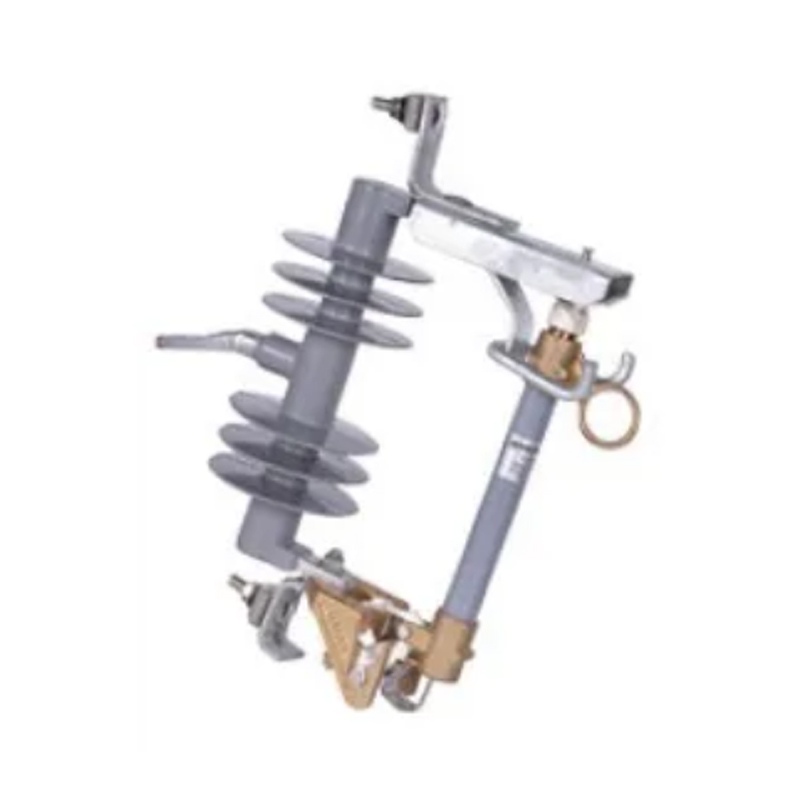
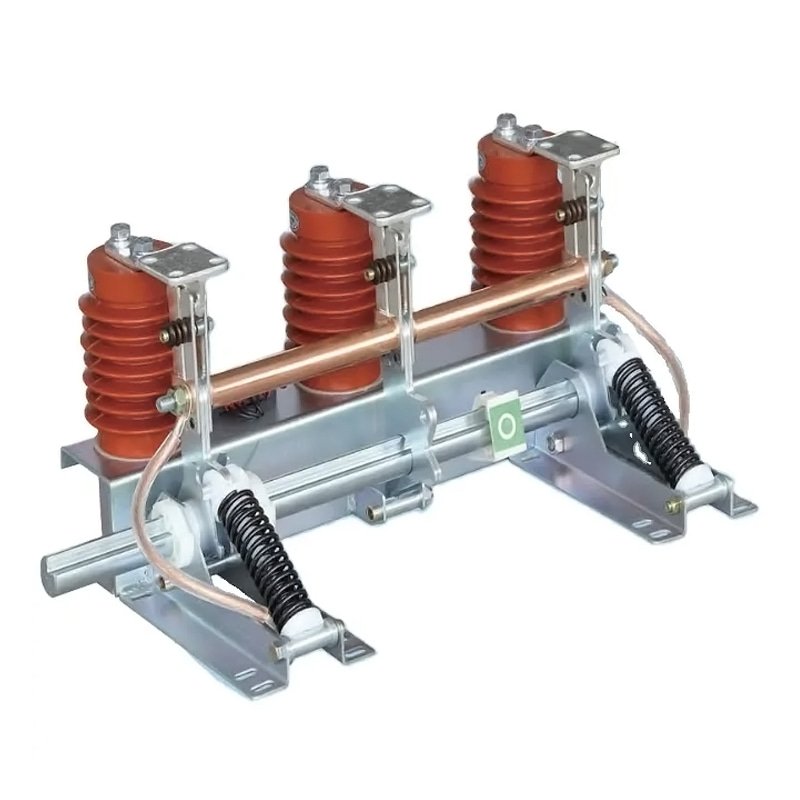
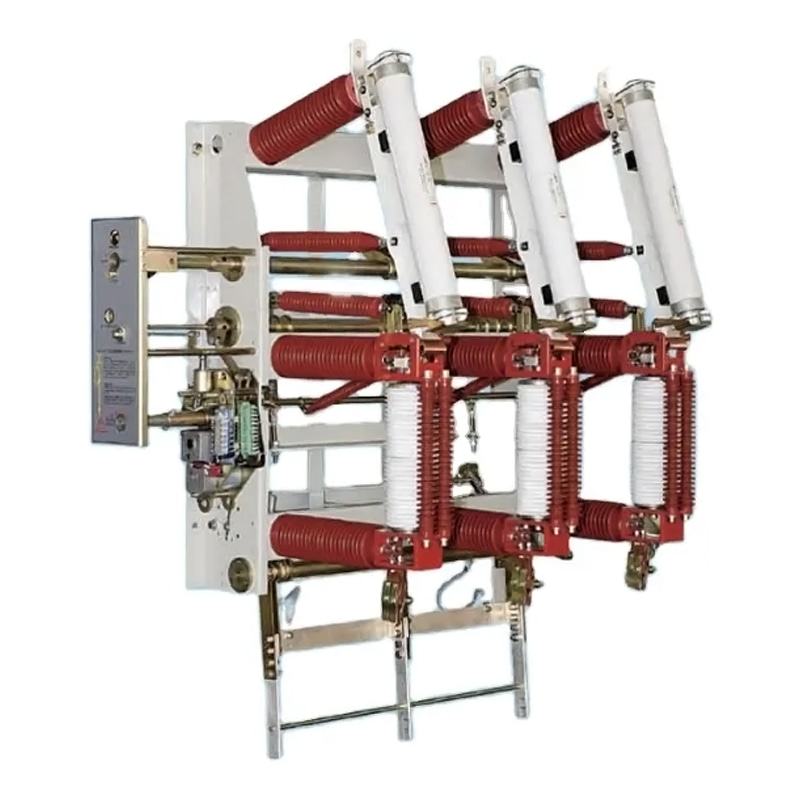
The modern power grid is a complex network that requires sophisticated protection measures to ensure its stability and reliability. One of the critical components in safeguarding electrical infrastructure from the damaging effects of voltage surges is the surge arrester.
Surge arresters are critical components in electrical systems designed to protect sensitive equipment from voltage spikes or surges. These devices are connected to the power lines and are capable of absorbing excessive voltage without being damaged themselves. They operate by providing a low-impedance path for the surge to follow, thus diverting it away from the protected equipment.
There are various types of surge arresters, including metal oxide varistors (MOV), silicon carbide, and gas discharge tubes, each with its own characteristics and applications. High Voltage Surge Arresters are typically used in transmission and distribution systems, while Electrical Surge Arresters and Power Surge Arresters are more commonly found in industrial and residential settings.
Proper selection and installation of surge arresters are essential to ensure they can effectively handle the big surge current that the system might experience. Regular maintenance and testing are also crucial to guarantee their continued performance and reliability.
Surge arresters are devices designed to protect electrical equipment from overvoltage transients. These transients can be caused by lightning strikes, switching operations, or other system disturbances. If left unchecked, these surges can lead to equipment failure, service interruptions, and even catastrophic damage to critical infrastructure.
High Voltage Surge Arresters are specifically engineered to handle the high-energy demands of high voltage systems. They are typically installed in substations and are connected in parallel to the equipment they protect. HVSAs operate by providing a path of least resistance for the surge to follow, diverting it away from sensitive equipment. This ensures that the voltage across the protected equipment remains within safe operating limits.
Electrical Surge Arresters are used across a range of applications, from low-voltage residential systems to medium-voltage industrial applications. They are designed to protect against voltage spikes that can originate from within the electrical system itself, such as those caused by the switching of heavy loads or the operation of motors and transformers. ESAs are crucial for maintaining the safety and performance of electrical systems by preventing damage to components like circuit breakers, switches, and control panels.
Power Surge Arresters are a type of surge protection device that is commonly used in power distribution systems. They are designed to protect power lines and transformers from the effects of power surges. PSAs are particularly important in areas prone to lightning strikes, as they can absorb the high-energy surges and prevent them from traveling down the power lines and causing widespread damage.
The technology behind surge arresters is continuously evolving to meet the growing demands of modern power systems. New materials and designs are being developed to improve the performance and reliability of these devices. For instance, the use of metal-oxide varistors (MOVs) has become widespread due to their ability to handle high surge currents without significant degradation.
Surge arresters must comply with various international standards to ensure their effectiveness and safety. Standards such as IEEE C62.11, IEC 60099, and IEEE C62.22 set guidelines for the design, testing, and application of surge arresters. Compliance with these standards is crucial for the proper functioning of surge arresters and the protection they provide.



 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى