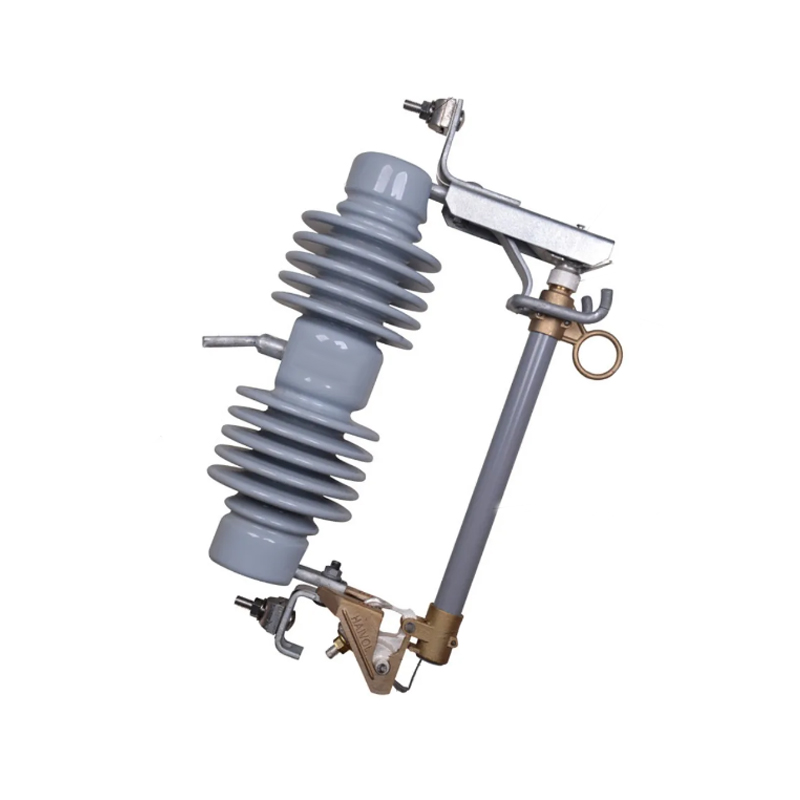
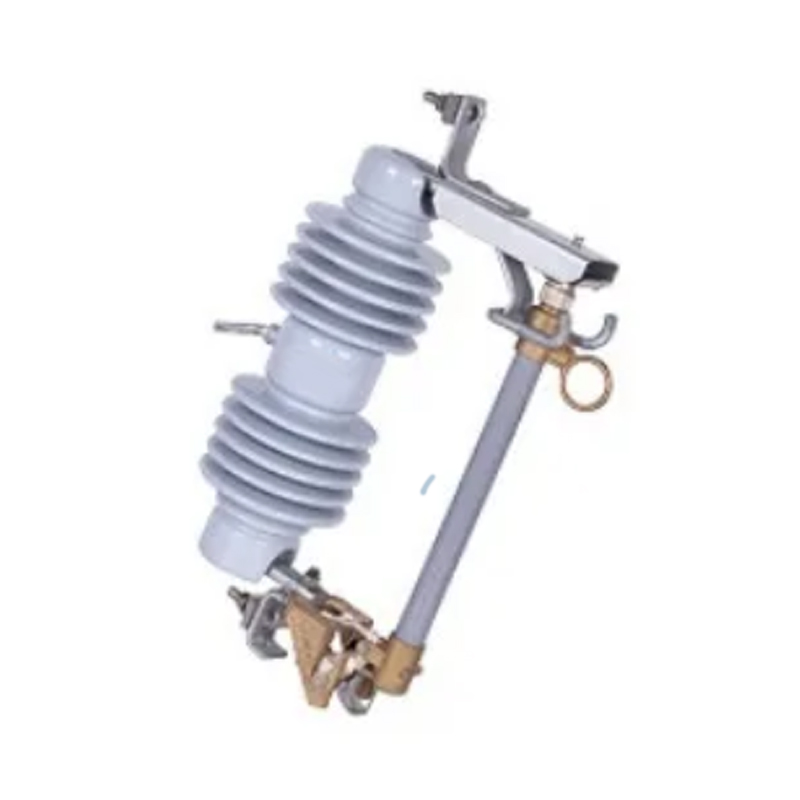
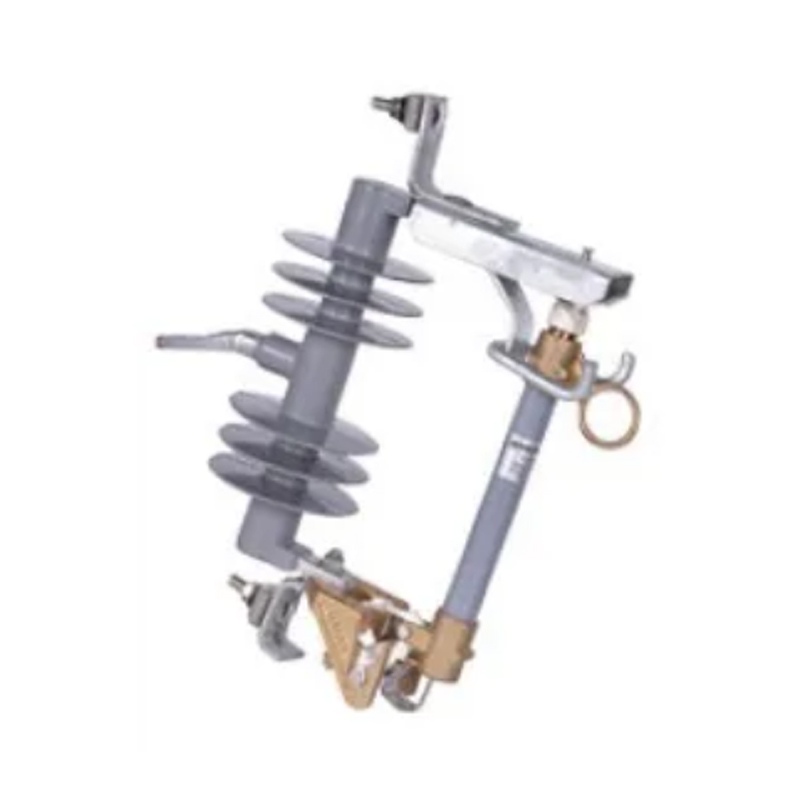
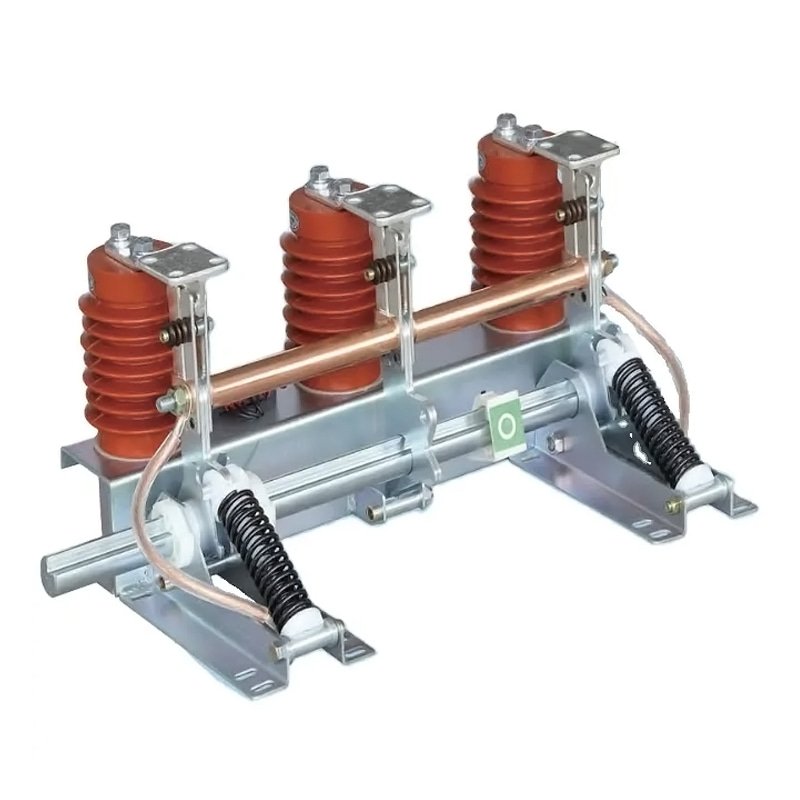
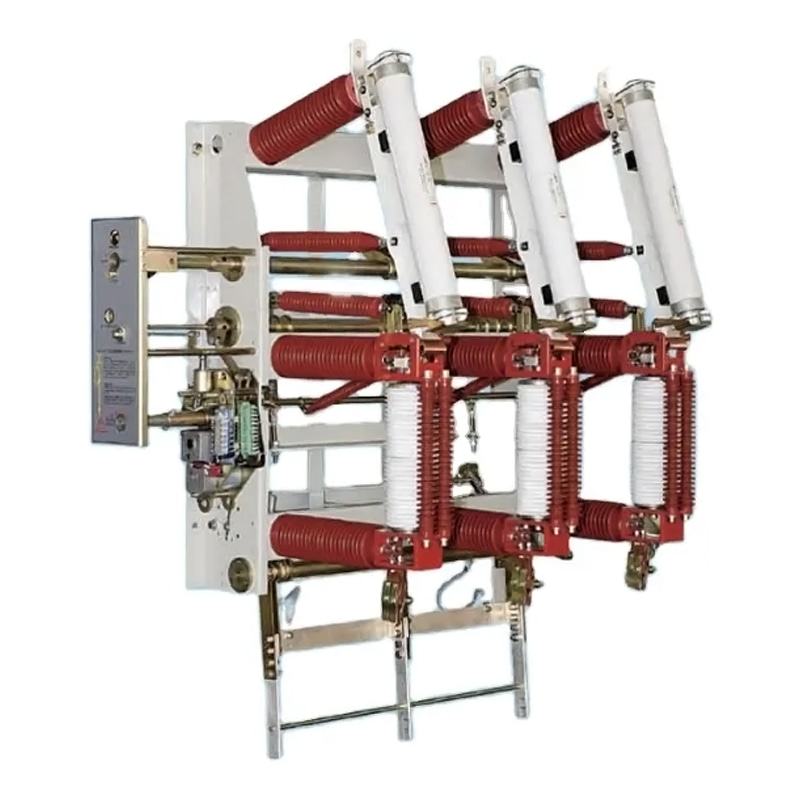
In the realm of electrical power distribution, load break switches play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and reliability of the grid. These switches are designed to interrupt the flow of current under load conditions, allowing for maintenance, testing, and the addition or removal of electrical components.
Sulfur Hexafluoride (SF6) is a colorless, odorless, non-toxic, and non-flammable gas that has excellent insulating and arc-quenching properties. It is widely used in the electrical industry for high-voltage switchgear due to its high dielectric strength.
SF6 load break switches are composed of an insulating enclosure filled with SF6 gas, which serves as an insulating medium and aids in extinguishing arcs during switching operations. The switch typically includes a moving contact and a stationary contact, which are separated to interrupt the current flow.
- High dielectric strength: SF6 provides predominant insulation compared to air or oil, allowing for compact switchgear designs.
- Arc-quenching capabilities: The gas effectively extinguishes arcs, reducing the risk of damage to the switchgear.
- Environmentally friendly: SF6 is non-toxic and non-flammable, making it a safer choice for indoor installations.
SF6 load break switches are commonly used in medium voltage networks for applications such as:
- Disconnecting and making circuits under load conditions.
- Providing isolation for maintenance and testing purposes.
- Switching between power sources in distribution networks.
Load break switch transformers are a specialized type of transformer that incorporates a load break switch within its design. This allows for the transformer to be disconnected from the electrical grid without the need for additional switchgear.
These transformers are designed with a built-in load break switch, which can be operated remotely or manually. The switch is typically located at the high-voltage side of the transformer, ensuring safe disconnection under load conditions.
- Space-saving: The integrated switch eliminates the need for separate switchgear, reducing the overall footprint of the installation.
- Cost-effective: Combining the switch and transformer into a single unit can reduce material and installation costs.
- Enhanced safety: The built-in switch allows for safer disconnection and reconnection of the transformer to the grid.
Load break switch transformers are ideal for applications such as:
- Substations where space is at a premium.
- Industrial facilities requiring reliable power supply with easy disconnection options.
- Utility networks where transformer replacement or maintenance is frequent.
11kV load break switches are designed to operate at a nominal voltage of 11 kilovolts, making them suitable for medium voltage applications.
These switches are built to handle the specific voltage and current requirements of 11kV systems. They are equipped with features such as:
- High-voltage insulation to withstand the electrical stress of 11kV.
- Adequate arc-quenching mechanisms to ensure safe operation.
- Robust mechanical linkages for reliable switching action.
When operating an 11kV load break switch, it is essential to consider factors such as:
- The type of load being switched (e.g., inductive, resistive, or a combination).
- The big current that the switch can safely interrupt.
- The ambient conditions, including temperature and altitude, which can affect the switch's performance.
11kV load break switches are widely used in various electrical systems, including:
- Medium voltage distribution networks for load switching and isolation.
- Industrial and commercial facilities requiring controlled power distribution.
- Utility substations for efficient grid management and maintenance.
Load break switches, whether they are SF6-based, integrated into transformers, or designed for 11kV systems, play a vital role in the safe and efficient operation of electrical power systems. Understanding the unique features and applications of each type of switchgear is crucial for engineers and technicians responsible for the design, installation, and maintenance of electrical infrastructure.



 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى