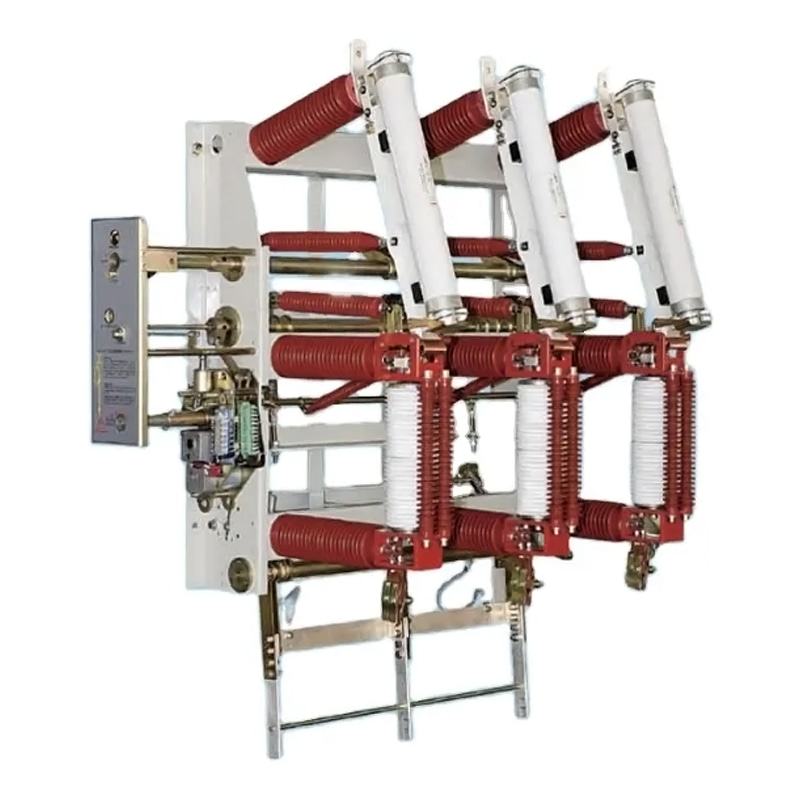
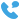
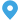
The backbone of any modern electrical grid is its high-voltage transmission and distribution network. These systems are responsible for the efficient transfer of electrical power from generation facilities to the end consumers. High-voltage transmission distribution substations play a pivotal role in this process, acting as critical nodes that manage and control the flow of electricity across vast distances.
Substations are integral to the power grid, serving multiple functions that include:
1. Stepping Up and Stepping Down Voltages: They adjust voltage levels to match the requirements of the transmission lines and the end-user equipment.
2. Protection: They incorporate various protective devices to safeguard the grid from faults and surges.
3. Control: They facilitate the control and monitoring of the power flow, ensuring stability and reliability.
4. Redistribution: They allow for the redistribution of power to different areas of the grid as needed.
A typical high-voltage substation consists of several key components:
1. Transformer: The heart of the substation, transformers are used to convert voltage levels from high to low and vice versa.
2. Circuit Breakers: These devices are crucial for safety, as they can interrupt the flow of electricity in case of a fault.
3. Switchgear: This includes various types of switches and protective devices that control the flow of power.
4. Busbars: They are the conductive paths that connect different components within the substation.
5. Instrument Transformers: These are used for measuring and monitoring the power levels within the substation.
6. Control Systems: Modern substations are equipped with advanced control systems for automated operation and remote monitoring.
Designing a high-voltage substation involves several critical considerations:
1. Load Forecasting: Accurate predictions of future power demands are essential for proper planning.
2. Reliability: The design must ensure that the substation can operate reliably under various conditions.
3. Safety: Safety measures must be incorporated to protect both personnel and equipment.
4. Environmental Impact: The substation should be designed with small environmental impact in mind.
5. Cost-Effectiveness: Economic considerations are vital, as the substation must be cost-effective to build and maintain.
With the advent of smart grid technology, high-voltage substations are becoming increasingly sophisticated:
1. Automation: Automated systems can manage the substation more efficiently, reducing the need for manual intervention.
2. Smart Sensors: These provide real-time data on the substation's performance, allowing for proactive maintenance.
3. Communication Systems: Advanced communication systems enable better coordination between substations and the control center.
4. Integration with Renewables: Modern substations are designed to integrate seamlessly with renewable energy sources.
Regular maintenance is crucial for the longevity and reliability of high-voltage substations:
1. Inspection: Regular inspections help identify potential issues before they become critical.
2. Preventive Maintenance: This includes routine checks and replacements of components to prevent failures.
3. Upgrading: As technology advances, substations may need to be upgraded to incorporate new features and improvements.
High-voltage substations face several challenges:
1. Corrosion: Exposure to the elements can lead to corrosion of metal components.
2. Wildlife Interference: Animals can cause damage or pose a threat to the operation of the substation.
3. Cybersecurity: With increased automation and digitalization, substations are vulnerable to cyber threats.
Solutions to these challenges include:
1. Use of Corrosion-Resistant Materials: Selecting materials that are less susceptible to corrosion can extend the life of the substation.
2. Wildlife Deterrents: Implementing measures to deter animals from entering the substation area.
3. Cybersecurity Measures: Establishing robust cybersecurity protocols to protect the substation's digital infrastructure.
High-voltage transmission distribution substations are complex and critical components of the power grid. They require careful planning, design, and maintenance to ensure the reliable and efficient delivery of electricity.



 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى