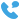
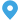
A transformer substation is an essential facility in electrical power distribution. It plays a vital role in reducing the voltage levels of electricity before it is delivered to homes, industries, and other consumers.
The primary function of a transformer substation is to step down high-voltage electricity to a lower voltage for distribution. This process is necessary because the electricity generated at power plants is typically at a very high voltage, which is not suitable for residential or commercial use. High-voltage transmission smalls energy loss during long-distance travel, but before reaching homes and businesses, the voltage must be reduced.
Transformer substations contain transformers that perform this vital step-down function. The transformers use electromagnetic induction to convert the voltage, ensuring the power can be safely used by consumers.

A typical transformer substation consists of several key components that work together to ensure the safe and efficient transmission of electricity:
Transformers: These are the core of the substation, responsible for changing the voltage levels. They come in various sizes and capacities, depending on the power needs of the area being served.
Circuit Breakers and Switchgear: These components protect the electrical system from faults, such as short circuits or overloads, by automatically disconnecting power when necessary. They help maintain the integrity of the grid and ensure safety during abnormal conditions.
Busbars: These are metallic bars that conduct electricity and connect different sections of the substation. They allow the power to be routed to different directions, ensuring continuous electricity supply to multiple consumers.
Capacitors and Reactors: These devices are used to manage the quality of electricity. Capacitors improve the power factor and help stabilize the voltage, while reactors are used to control the flow of electrical current in certain situations.
Control and Protection Systems: These systems monitor the substation’s performance and ensure the equipment operates within safe parameters. Control systems enable operators to remotely monitor and manage the substation, while protection systems identify and address potential faults.
Transformer substations are crucial in ensuring that electricity is distributed efficiently and safely to the end user. Without substations, it would not be possible to reduce the high voltage from power plants to usable levels for homes and businesses. These substations also contribute to the stability of the electrical grid by regulating power flow and providing protection from faults and overloads.
In addition, transformer substations enable the efficient delivery of electricity over long distances. High-voltage transmission lines small energy loss, and substations ensure that power is delivered in a form that is safe and appropriate for use in various environments. This makes substations a critical component of the entire power distribution system.
As the demand for electricity continues to grow, transformer substations will remain central to the development of power distribution systems. Advances in technology may pilot more efficient, compact, and sustainable substations that can handle the increasing demands of modern energy systems. Moreover, as renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power are integrated into the grid, transformer substations will play a key role in adapting to these new energy flows.
Transformer substations are essential for the safe and efficient distribution of electricity. By reducing high-voltage power to levels suitable for everyday use, substations ensure that consumers receive a stable, reliable, and safe electricity supply. Their role in the electrical grid cannot be overstated, and as energy demands evolve, transformer substations will continue to adapt to meet future challenges.



 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى