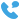
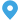
Transformer substations are critical components in modern power systems, playing a vital role in the transmission and distribution of electrical energy. They are designed to transform voltage levels, ensuring that electricity can be efficiently transmitted over long distances and safely distributed to consumers.
A transformer substation is a facility where electrical transformers are housed to change the voltage levels of alternating current (AC) power. These substations are strategically located throughout power grids to facilitate the efficient transmission and distribution of electricity. The primary function of a transformer substation is to step up or step down voltage levels, depending on the requirements of the power grid.

The core component of a substation, transformers are responsible for changing voltage levels. Step-up transformers increase voltage for transmission over long distances, while step-down transformers reduce voltage for safe distribution to consumers.
This equipment is used to control, protect, and isolate electrical circuits. Switchgear includes circuit breakers, disconnect switches, and fuses, which help manage electrical flow and protect against faults.
These are conductive bars that distribute electrical power within the substation. They connect transformers, switchgear, and other components, ensuring efficient power flow.
Modern substations are equipped with advanced control systems that monitor and manage operations. These systems can detect faults, adjust voltage levels, and ensure the substation operates within safe parameters.
Transformer substations serve several critical functions in the power grid, ensuring the reliable and efficient transmission and distribution of electricity.
One of the primary functions of a transformer substation is to transform voltage levels. High voltage is necessary for long-distance transmission because it reduces energy losses due to resistance in the transmission lines. However, high voltage is not safe for residential or commercial use. Substations step down the voltage to levels suitable for distribution to homes and businesses.
Transformer substations play a crucial role in distributing electricity to different areas. They receive power from generating stations or transmission lines and distribute it to local networks. This distribution ensures that electricity reaches consumers reliably and efficiently.
Substations are equipped with switchgear and protective devices that detect and isolate faults. When a fault occurs, such as a short circuit or overcurrent, the switchgear can quickly disconnect the affected circuit. This action prevents damage to equipment and ensures the safety of personnel and the public.
Transformer substations contribute to the overall stability of the power grid. They help balance the load, ensuring that supply meets demand. Modern substations are often equipped with advanced control systems that can adjust voltage and power flow in real-time, enhancing grid stability and reliability.
Transformer substations are essential in various applications, from urban areas to remote locations. In cities, they ensure that electricity is distributed efficiently to meet the high demand of residential and commercial consumers. In rural areas, substations help extend the power grid, providing electricity to remote communities and supporting agricultural and industrial activities.
The design and operation of transformer substations also have environmental implications. Modern substations are designed to small their environmental footprint. They use energy-efficient transformers and are often equipped with systems to reduce emissions and noise pollution.
Transformer substations are indispensable components of modern power systems. They ensure the efficient transmission and distribution of electricity, provide critical fault protection, and contribute to system stability.



 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى