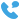
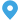
A transformer substation is a crucial component in the electrical power distribution system. It plays a vital role in adjusting the voltage levels of electrical power before it reaches consumers. These substations are used to step up or step down the voltage of electricity, ensuring that it is delivered efficiently and safely.
A transformer substation is an electrical facility that contains transformers used for changing the voltage level of electricity. The primary purpose of a transformer substation is to either increase (step up) or decrease (step down) the voltage of the electrical power coming from the power generation plant before it is sent to the transmission lines or distributed to homes and businesses.

A typical transformer substation includes various electrical components such as transformers, circuit breakers, isolators, switchgear, busbars, and protection devices. These components work together to ensure the safe and efficient operation of the substation. The power enters the substation at a certain voltage, and through the transformer, the voltage is adjusted to meet the needs of the consumers or the requirements of the power transmission system.
Transformer substations can be broadly classified based on their function and design. Some common types include:
Step-Up Transformer Substations: These substations increase the voltage of electrical power generated at the power plant. The higher voltage allows the power to travel over long distances with minimal loss of energy. Step-up substations are typically located at or near power generation plants.
Step-Down Transformer Substations: These substations reduce the voltage of the power received from transmission lines before it is distributed to consumers. Step-down substations are generally located closer to residential, commercial, and industrial areas.
Distribution Substations: These substations are responsible for further reducing the voltage levels before electricity is supplied to homes and businesses. They step down the voltage to a level suitable for end-users.
Substations for Special Applications: Some transformer substations are designed for specialized uses, such as those required in industrial plants, renewable energy systems, or high-voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission systems.
Several key components are found in a typical transformer substation:
Transformers: The transformer is the central component of the substation, responsible for stepping up or stepping down the voltage levels. It consists of primary and secondary windings that are electrically isolated from each other while allowing power to be transferred between them.
Circuit Breakers: These devices protect the electrical network by interrupting the flow of current in the event of a fault or overload. Circuit breakers are essential for maintaining the safety of the substation and preventing damage to other components.
Switchgear: Switchgear allows operators to control, protect, and isolate electrical equipment within the substation. It includes switches, fuses, and relays that enable the switching of electrical circuits.
Busbars: These are metal bars that serve as conductors for distributing electricity within the substation. Busbars can carry large amounts of electrical current and are used to connect various components of the substation.
Protection Devices: These devices monitor the electrical system and automatically disconnect the substation from the power grid in case of faults or irregularities. They ensure that the substation operates safely and reliably.
Transformer substations are a vital part of the power distribution network, ensuring the proper delivery of electricity at the right voltage levels. They serve the important function of stepping up or stepping down voltage, making them crucial for energy efficiency, safety, and reliability in power systems.



 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى