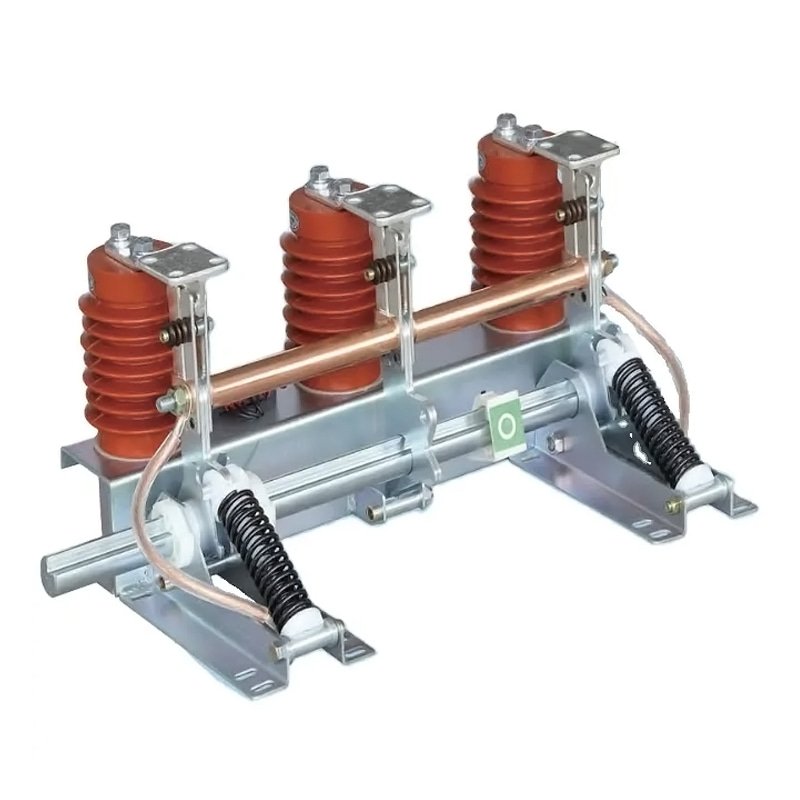
Design Sale Vacuum Circuit Breaker Manufacturing Supplier Maker
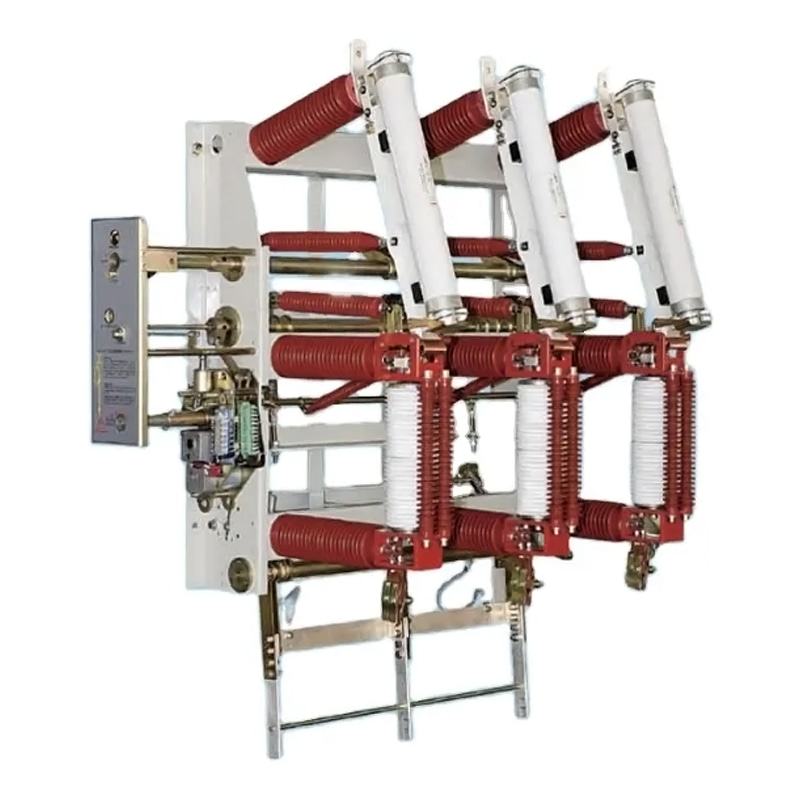
The heart of any electrical system lies in its ability to manage and control the flow of power safely and efficiently. Vacuum circuit breakers are integral to this process, serving as automatic electrical switches that protect circuits from damage due to overcurrent conditions. These devices are designed to ensure the reliability and safety of electrical systems in various applications, from residential to industrial settings.
At the core of a vacuum circuit breaker is its ability to make, carry, and break currents under normal circuit conditions. Additionally, they are capable of interrupting currents under abnormal conditions, such as those caused by short circuits. The primary function of a vacuum circuit breaker can be summarized as follows:
1. Current Interruption: The breaker interrupts the flow of current when an overcurrent condition is detected, preventing damage to the electrical system.
2. Arc Suppression: Utilizing the properties of a vacuum, the breaker effectively suppresses electrical arcs, which are the primary cause of damage during a fault.
3. Contact Material: The choice of contact material is crucial for the longevity and performance of the breaker. Materials with high electrical conductivity and arc resistance are typically used.
The operational mechanism of a vacuum circuit breaker involves several key components:
1. Vacuum Chamber: The vacuum chamber houses the contacts and is designed to maintain a high vacuum, which facilitates the interruption of current flow.
2. Contacts: The contacts are the conductive parts that are close to allow current flow and open to interrupt it. They are made of materials that can withstand the high temperatures generated during arcing.
3. Actuator: The actuator is responsible for the mechanical operation of the breaker, opening and closing the contacts in response to control signals.
4. Arc Chute: In the event of a fault, the arc chute helps to cool and extinguish the arc, ensuring safe operation.
Vacuum circuit breakers can be classified based on their application and design:
1. Outdoor Vacuum Circuit Breakers: Designed for outdoor applications, these breakers are built to withstand various weather conditions.
2. Indoor Vacuum Circuit Breakers: These are used in indoor environments and are typically smaller in size compared to outdoor breakers.
3. High Voltage Vacuum Circuit Breakers: Used in high voltage applications, these breakers are designed to handle the high electrical stresses associated with such systems.
The use of vacuum circuit breakers offers several advantages over other types of circuit breakers:
1. Long Lifespan: The absence of moving parts in contact with air or oil leads to a longer operational life.
2. Low Maintenance: Due to the sealed vacuum environment, vacuum circuit breakers require small maintenance.
3. High Reliability: The vacuum environment ensures consistent performance, even in harsh conditions.
4. Environmental Friendliness: Unlike oil-filled breakers, vacuum breakers do not pose a risk of oil leakage, making them more environmentally friendly.
Vacuum circuit breakers are used in a wide range of applications due to their robustness and reliability:
1. Power Distribution: In power distribution systems, vacuum breakers ensure the safe and efficient distribution of electricity.
2. Industrial Automation: In industrial settings, these breakers provide reliable protection for automated machinery and processes.
3. Renewable Energy: Vacuum circuit breakers are used in solar and wind energy systems to protect against electrical faults.
Vacuum circuit breakers are a testament to the evolution of electrical protection technology. Their ability to provide reliable and safe electrical protection makes them an indispensable component in modern electrical systems. As technology continues to advance, the role of vacuum circuit breakers is expected to expand, further enhancing the safety and efficiency of electrical power management.



 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى